Abstract
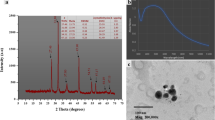
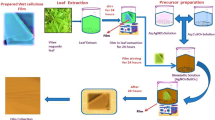
In this study, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were in situ generated on the surface of cellulose matrix using leaf extract of cissampelos pareira (LCP) by environmentally benign green synthesis. The morphological and structural properties of synthesized cellulose silver nanocomposites (Cel/LCP/Ag-NCs) were characterized by different spectral studies such as UV–visible spectroscopy, SEM, TEM, FT-IR, AFM, DRS, PL, Lifetime, XPS and XRD. Silver nanoparticles were obtained in the cellulose matrix with an average size of 34.26 nm and with antioxidant activity which has been evaluated by ABTS (70.34% at 100 µg/mL) and DPPH (81.65% at 100 µg/mL) methods. The antimicrobial properties of cellulose, Cel/LCP, Cel/LCP (10 mM, 30 mM and 50 mM AgNO3), tested on 13 microorganisms were determined using disk diffusion method. The most effective nanocomposites (Cel/LCP/10, 30 and 50 mM AgNO3), Cel/LCP/50 mM AgNO3 afforded the best antimicrobial properties because increasing the concentration of AgNO3 solution, the zone of inhibition also increased. The prepared cellulose silver nanocomposites synthesized by leaf extract of cissampelos pareira shows the potential to be applied in the future development of therapeutics and biomedical applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishna Gudikandula and SingaraCharya Maringanti (2016). Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical and biological methods and their antimicrobial properties. Journal of Experimental Nanoscience 11, 714–721.
AnsarMehmood HumaYousaf, KhawaiaShafique Ahmad, and Muhammad Raffi (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications as an alternative antibacterial and antioxidant agents. Materials Science and Engineering C 112, 110901.
SeyedehFatemeh Hashemi, Nooshin Tasharrofi, and MohaddesehMahmoudi Saber (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using teucrium polium leaf extract and Assessment of their antitumor effects against MNK45 human gastric cancer cell line. Journal of Molecular structure 1208, 127889.
Zannatual Ferdous and Abderrahim Nemar (2020). Health impact of silver nanoparticles: a review of the biodistribution and toxicity following various routes of exposure. Inernational journal of molecular science 21 (7), 2375.
Shubhra Rajput, Dinesh Kumar, and Veena Agrawal (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Indian Belladonna extract and their potential antioxidant, antiinflammatory, anticancer and larvicidal activities. Plant Cell reports 39 (7), 921–939.
Aida Fadakar Sarkandi, Majid Montazer, Tina Harifi, and MahnazMahmoudi Rad (2020). Innovative preparation of bacterial cellulose/silver nanocomposite hydrogels: In situ green synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 138 (6), 49824.
M. Kishanji, G. Mamatha, K. Obi Redy, Varada Rajulu, and K. Madhukar (2017). In situ generation of silver nanoparticles in cellulose matrix using azadirachta indica leaf extract as a reducing agent. International Journal of Polymer Analysis and Characterization. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2017.1369612.
V. Sadanand, N. Rajini, B. Satyanarayana, and A. Varada Rajulu (2016). Preparation and properties of cellulose/silver nanoparticle composites with in situ-generated silver nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum leaf extract. International Journal of Polymer Analysis and Characterization 21 (5), 408–416.
M. Ajaib, F. Shafi, S. A. Mirza, and M. A. Iqbal (2018). Evaluation of the antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of cissampelos pareira. Pakistan Journal of Science 70 (3), 239.
M. Ganguly (2007). Antifertility activity of the methanolic leaf extract of cissampelos pareira in femal albinomice. J Ethnopharmacopl 11 (3), 688–691.
Johnatan Wellisson da Silva Mendes, Walmir Emanuel Miranda. Cunha, and Jose Galberto Martins. da costa (2020). cissampelos genus: biological activities, ethnobotanical and phytochemical aspects. Phytochemistry Reviews 19, 955–982.
Arti Gupta, D. R. Sonia Pandey, N. R. Shah, and J.S. Yadav. Seth (2011). Pharmacognostical and phytochemical evaluation of leaves of cissampelos pareira. Pharmacognosy journal 3, 21.
Irmma Ramrez, Alfredo Carabot, Pablo Melendez, Juan Carmona, Manuel Jimenez, Asmita V. Patel, A. Trevor, Gerald Blunden Crabb, D. Pter, Simon L. Carry, and Manuel Costa Croft (2003). Cissampeloflavone, a chalcone-flavone dimer from Cissampelos pareira. Phytochemistry 64, 645–647.
A. I. Journal, P. Johnson, V. Krishnan, C. Loganathan, K. Govindhan, V. Raji, P. Sakayanthan, S. Vijayan, and T. Palvannan (2018). Rabid biosynthesis of bauhinia variegata flower extract - mediated silver nanoparticles: an effective antioxidant scavenger and amylase inhibitor. Artif. Cellsnomed. Biotechnol 46, 1488.
J. Banerjee and R. T. Narendhirakannan (2011). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from syzygiumcumini (L) seed extract and evaluation of their in vitro antioxidant activities. J. Nanomat. Biostruct 6, 961–968.
A. Guptha, D. J. Keddie, V. Kannappan, H. Gibson, I. R. Khalil, M. Kowalczuk, C. Martin, X. Shuai, and I. Radecka (2019). Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose hydrogelloaded with curcumin encapsulated in cyclo dextrins as wound dressing. Euru Polym J 118, 437–450.
R. Konwarh, B. Gogoia, R. Philip, M. A. Laskar, and N. Karaka (2011). Biomimetic preparation of polymer-supported free radical scavenging, cytocompatible and antimicrobial green silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of citrus sinensis peel. Colloid Surf B 84, 338–345.
S. Mowafi, H. Kafafy, A. Karima, A. Haggag, and R. M. Mohamed (2018). Facile and environmental benign in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for multi functionalization of wool fibers. Environ Sci Pollut Rese. 25, 29054–29069.
Zdenka Balaz, Imrich Strapac, Matej Bala, and Aneta Salayova (2020). A brief overview on antioxidant activity determination of silver nanoparticles. Molecule 25, 3191–29069.
Jie Cai and Lina Zhang (2005). Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol. Biosci 5, 539–548.
A. Serpen, E. Capuana, V. Fogliano, and V. Gokmen (2007). New procedure to measure the antioxidant activity of insoluble food components. J Agric Food Chem 55, 7676–7681.
C. H. Chen, C. H. Chia, S. Zakaria, M. S. Sajab, and X. Chin (2015). Cellulose nanofibrils: a rapid adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue. RSC Adv 5, 18204–182012.
E. Smiechowicz, B. Niekraszewiz, P. Kulpinski, and K. Dzitko (2018). Antibacterial composite cellulose fibers modified with silver nanocomposites. Cellulose 25, 3499–3517.
J. Wu, Y. Zheng, W. Song, J. Luan, X. Wen, Z. Wu, and X. Chen (2014). In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles/bacterial cellulose composites for slow-released antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym 102, 762–771.
N. S. Alahmadi, J. W. Betts, T. Heinze, S. M. Kelly, A. Koschella, and J. D. Wadhawan (2018). Synthesis and antimicrobial effects of highly dispersed, cellulose-stabilized silver/cellulose nanocomposites. RSC Adv 8, 3646.
R. Singaravelan and S. B. Sudarsanlwar (2015). Electro chemical synthesis, characterization, phytogenic properties of silver nanoparticles. Applied Nanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0396-0.
J. F. Moulder, W. F. Stickle, P. E. Sobol, and K. D. Bombem. in J. Chastain (ed.), Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Eden Prairie, Minnesota, 1979), 184.
Chuang Liu, Dong Yang, Yuangui Wang, Jiafu Shi, and Zhongyi Jiang (2012). Fabrication of antimicrobial bacterial cellulose–Ag/AgCl nanocomposite using bacteria as versatile bio factory. J Nanopart Res 14, 1084.
S. Dahel, J. Meuthen, and W. Viol (2013). Adsorption of silver on cellobiose and cellulose studied with MIES, UPS, XPS and AFM. Cellulose 20, 2469–2480.
Rucha Desai, Venu Mankad, K. Sanjeev, and Prafulla K. Jha (2012). Size distribution of silver nanoparticles: UV-Visible spectroscopic assessment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett 4, 1.
S. S. R. Challa Kumar (ed.), UV-VIS and Photoluminescence Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterization (Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2013). ISBN 978-3-642-27594-4 (eBook) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27594-4
R. Joseph, Y. L. Shen, D. Sabato, A. J. Malicka, J. Fang, Z. Gryczynski, and I. Gryczynski (2002). Effects of Silver Island Films on Fluorescence Intensity, Lifetimes, and Resonance Energy Transfer. Analytical Biochemistry 301, 261–277.
S. Jain, G. Bhanjana, S. Heydarifard, N. Dilbaghi, M. M. Nazhad, V. Kumar, K. H. Kim, and S. Kumar (2018). Enhanced antibacterial profile of nanoparticle impregnated cellulose foam filter paper for drinking water filtration. Carbohyd Poly 202, 219–226.
Y. Xu, S. Li, X. Yue, and W. Lu (2018). Review of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)-Cellulose Antibacterial Composites. Bio Resources 13, 2150–2170.
A. W. Bauer, W. M. M. Kirby, J. C. Sherris, and M. Truck (1966). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol 45, 493.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanmugam, C., Sivasubramanian, G., Govindhan, P. et al. Antimicrobial and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Cellulose/Silver-Nanocomposites with In Situ Generated Silver Nanoparticles Using Cissampelos Pareira Leaf Extract. J Clust Sci 33, 1727–1737 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02097-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02097-2