No products in the cart.
Return To Shop- Ceylon Grocery
Oops, looks that mega-menu was not imported correctly. Go to Appearance > Menus > edit menu and use the 8theme menu options to select the Static Block for this menu item and show the mega-menu content
- Ceylon Spicy
Oops, looks that mega-menu was not imported correctly. Go to Appearance > Menus > edit menu and use the 8theme menu options to select the Static Block for this menu item and show the mega-menu content
- Decor and appliance
Oops, looks that mega-menu was not imported correctly. Go to Appearance > Menus > edit menu and use the 8theme menu options to select the Static Block for this menu item and show the mega-menu content
- Health & Wellness
- Beauty and Care
- Ceylon Fashion
- Ceylon Instruments
Oops, looks that mega-menu was not imported correctly. Go to Appearance > Menus > edit menu and use the 8theme menu options to select the Static Block for this menu item and show the mega-menu content
- SL innovations
- Dashboard
- Store List
- My Orders
- Show more
0
$0.00
0
No products in the cart.
Return To Shop
Shopping cart (0)
Subtotal: $0.00
Congratulations! You've got free shipping.
You may be interested in…
Sale
Sale
New Igini Tea (Strychnos potatorum Tea/Clearing Nut Tea)
$47.88 $38.30
100g
This herbal tea is known for its impressive health benefits. Igini Tea supports kidney function, helping to flush out toxins and promoting urinary health. It also aids in regulating blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for maintaining healthy glucose levels.
Furthermore, Igini Tea soothes the digestive system, providing relief from indigestion and bloating. Additionally, it acts as an appetite booster, stimulating hunger for those
experiencing a lack of appetite. Brew a cup or two of Igini Tea daily and savor its refreshing
taste while reaping the rewards of its natural properties. Embrace a healthier lifestyle with the
goodness of Igini Tea. Remember to store it in a cool, dry place to preserve its freshness.
Elevate your well-being with the revitalizing benefits of Igini Tea


Health benefits of Clearing Nut/Igini/Strychnos potatorum
| Clearing Nut Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Clearing Nut |
| Scientific Name: | Strychnos potatorum |
| Origin | Tropical Africa, tropical Asia, eastern India, eastern Myanmar, southern and central parts of India, Sri Lanka and Burma |
| Colors | Green when young turning to dark blue when ripe |
| Shapes | Globose berry, 16-18 mm in diameter, soft, blue-black, spherical, pericarp hard |
| Flesh colors | Purplish |
| Taste | Bitter, astringent, sweet |
| Health benefits | Treat eye diseases, Anti-microbial, Treat skin problems, Antioxidants, Treating Jaundice, Improve digestion, Anti-inflammatory, Regulate blood glucose level, Boost immunity |
Strychnos potatorum regularly known as Clearing Nut or Water filtering natural product is a deciduous tree having a place with family Loganiaceae. The plant is local to tropical Africa, tropical Asia, eastern India, and eastern Myanmar, southern and focal pieces of India, Sri Lanka and Burma. Clearing nut, Clearing nut tree, Induga, Water purifying fruit, Chillam, Mudanhapfunye, Nirmali, Tattan Kottei, Black bitterberry, Grape strychnos, Umlombelombe, water-filter nut, Ambu-prasada, Chillachettu, Chilladabeeja, Chillaginjalu, Chilu, and Dupa are some of the more common names for the The plant has different nearby restorative purposes and is additionally utilized locally to explain water before drinking it. In local markets, the seeds are sold as a water purifier. In India and Myanmar, the tree’s seeds are frequently utilized for water purification and traditional medicine. Polysaccharide gum, which is useful in the paper and textile industries, can be found in abundance in seeds.
Clearing Nuts Facts
| Name | Clearing Nut |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Strychnos potatorum |
| Native | Tropical Africa, tropical Asia, eastern India, eastern Myanmar, southern and central parts of India, Sri Lanka and Burma |
| Common Names | Ambu-prasada, Chillachettu, Chilladabeeja, Chillaginjalu, Chilu, Clearing nut, Dupa, Gajrah, Induga, Indupachettu, Iriya, Kataka, Katakami, Kotaku, Kuchla, M’tupa, Mitupe, Neimal, Nelmal, Nirmali, Tetan-kotai, Tetran-paral, Tetta, Tettamparel, Tettan cottay marum, Tettran, Toillaghenjaloo, Water-filter nut, chilla, chillikavi, cleaning nuts, clearing nut, clearing-nut tree, clearing-nut-tree, grape strychnos, ingini, kataka, kataka, katakam, kottai, nirmal, nirmali, nirmaliträd, payah prasadisa, tetramabaral |
| Name in Other Languages | Bengali: Nirmali (নির্মলী) Burmese: Hk paungg raykyi pain (ခပေါင်းရေကြည်ပင်) English: Clearing nut, Clearing nut tree, Induga, Water purifying fruit, Chillam, Mudanhapfunye, Nirmali, Tattan Kottei, Black bitterberry, Grape strychnos, Umlombelombe, water-filter nut French: Noix floculante, Noix tamoule, Tetamcottai, Tetâmaram Gujarati: Nirmali (નિર્મલી) Hindi: Nirmali (निर्मली), Neimal, Nelmal Irula: Sillamaram Kannada: Chilladabeeja, Chilu, Chilla (ಚಿಲ್ಲ) Malayalam: Tetranparal, Tetraparel, tēṟṟāmparal (തേറ്റാമ്പരൽ), Chillam, Kadakam, Thettamaram, Thettamparel, Thettamaram Marathi: Chilbing, Chilhara, Gajara, Nirwali Myanmar: Khabaung yay-kyi, mango-taukpa-tit Nepali: Damaai Phal (दमाई फल), Nirmali (निर्मली) Oriya: Kotaku Punjabi: Niemali Sanskrit: Katak, Kataka, Kataka ambuprasada, Ambuprasadani, Ambuprasadanaphala, Chakshushya, Chh edaniya, Guchhaphala, Kata, Kataka, Katakarenu, Kattha, Khataka, Lekhanatmaka, Payaprasadi, Ruchishya, Ruchya, Rushya, Shlakshna, Shodanatmaka, Tiktamaricha, Tiktaphala, Toyaprasadana Shona: Mudanhapfunye, Mudyagudo, Mudyakuwe, Mudyambira Swedish: Nirmaliträd Tamil: Tetamkotai, Tetankotai, Tetta, Tettamaram, Tettran, Terra (தேற்றா), Kalkottai, Kal Kottei, Sillamaram, Sirungamaram, Sirungaru Maram, Tattan Kottei, Thetthamkottai, Sirungamaram, Kal Kottei, Tattan Kottei, Sillamaram, Sirungaru Maram, Kalkottai Telugu: Chillachetu, Indupachettu, Iṇḍupu (ఇండుపు), Cillagin̄ja (చిల్లగింజ), Chilla-gingalu Urdu: Nirmali |
| Plant Growth Habit | Deciduous much-branched shrub or small to medium-sized glabrous tree |
| Growing Climates | Gallery forest, brachystegia woodland, semi evergreen bush land, river banks, banks of dry riverbeds, on termitaries, in dry woodland, along dry water courses and on termite mounds |
| Plant Size | Up to 12 m upon maturity with bole growing up to 100 cm in diameter |
| Stem | Fluted and covered with black, thick, square to rectangular scales. |
| Bark | Bark is 1.32 cm thick, black or brownish-black, corky, with very deep and narrow vertical, thin ridges, which easily break off. Branches are swollen at nodes. |
| Branchlets | Branchlets are pale to dark brown, glabrous, apex modified into a spine-like tip 1–3 mm long. |
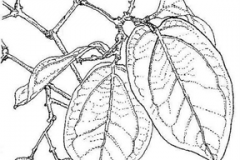
| Leaf | Leaves are simple, opposite, estipulate; leaf-stalk 2-8 mm, hairless; blade is 5-15 cm long and 3.5-7.5 cm wide, elliptic, ovate, elliptic-ovate, base blunt or round, tip pointed, margin entire, hairless, shiny, papery. |
| Flowering season | February—May |
| Flower | Flowers are bisexual, regular, (4–) 5-merous, appearing before or with the young leaves. Sepals are fused at base, ovate to oblong, up to 2.5 mm long. Corolla tube is up to 3.5 mm long, lobes oblong, c. 4.5 mm long, acute, spreading, glabrous outside, inside with hairs on the base of the lobes, white, creamy or yellow |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Fruit is a sub-globose berry 12 – 18mm in diameter with a firm pericarp, black when ripe, containing 1 – 2 seeds in a whitish pulp |
| Fruit Color | Green when young turning to dark blue when ripe |
| Flesh | Purplish |
| Seed | Depressed-globose or ellipsoid, 10–13 mm × 9–13 mm × 6–9 mm, slightly glossy, pale brown with an obscure angular line all around, densely silky hairy, smooth |
| Taste | Bitter, astringent, sweet |
| Plant Parts Used | Roots, barks, seeds, fruit |
| Season | October—March |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
Clearing Nut Tree is a deciduous much-extended bush or little to medium-sized glabrous tree that typically grows up to 40 feet (12 meters) upon development with bole growing up to 100 cm in width. On termite mounds, in dry woodland, along dry watercourses, and in gallery forest, brachystegia woodland, semi-evergreen bush land, riverbanks, and banks of dry riverbeds, the plant can be found growing. Scales that are black and thick and square to rectangular in shape cover the fluted stem. The bark is corky, black or brownish-black, 1.32 cm thick, and it has very deep, narrow, vertical, thin ridges that are easy to break off. At the nodes, branches are swollen. The glabrous, pale to dark brown branchlets have an apex that has been modified into a spine-like tip that is between 1 and 3 millimeters long.
Leaves
The leaves are estipulate, simple, and opposite; leaf-tail 2-8 mm, smooth; The blade is elliptic, ovate, elliptic-ovate, base blunt or round, tip pointed, margin entire, hairless, shiny, and papery, and it measures 3.5-7.5 cm wide and 5-15 cm long. Nerves are 3-5 from the base, sidelong nerves from the midrib 4 sets, bald; prominent, veined intercostal net. The petioles are 2.5 mm long.
Flowers
Inflorescence is an axillary careless or clogged thyrse 1.5-2.5 cm long. Bisexual, regular, (4–) 5-merous flowers appear prior to or alongside young leaves. Sepals are ovate to oblong, fused at the base, and up to 2.5 mm long. The corolla tube is up to 3.5 millimeters long, has oblong, 4.5 millimeter-long, acute, spreading lobes, is glabrous on the outside and inside, and has white, creamy, or yellow hairs on the base of the lobes. Exserted stamens are inserted into the corolla tube’s mouth. The superior ovary is ovoid or conical, 1–2 mm long, glabrous, has two cells, and the style can be up to 4.5 mm long. The stigma is small, head-shaped, or sometimes obscurely has two lobes. Typically, flowering occurs between February and May.
Fruits
Prolific blossoms are trailed by a globose berry, 16-18 mm in width, delicate, blue-dark, round, pericarp hard; The pulp is smooth and purple. The seeds are smooth, densely silky-hairy, depressed, globose or ellipsoid, 10–13 mm long, 9–13 mm wide, slightly glossy, and surrounded by an obscure angular line.
Health benefits of Clearing Nuts
Listed below are some of the common health benefits of using clearing nuts
1. Treat eye diseases
The Clearing Nut has the potential to alleviate eye conditions. To treat a variety of eye conditions, the seeds of this plant are rubbed into a clean stone, and the paste is applied as eye shadow.
2. Anti-microbial
The Clearing Nut seeds were used to treat a variety of ailments, including infectious diseases, in folklore medicine. The utilization of seeds in conventional medication in one structure or the other requires a methodical assessment of its antibacterial as well as antifungal exercises. Late investigations show Clearing Nut seeds remove have critical bactericidal and fungicidal impacts.
3. Treat skin problems
Clearing Nuts is a notable spice in the Ayurvedic framework for treat skin sicknesses. To alleviate eczema and other skin conditions, the Clearing nuts root paste is applied to the skin. Applying the seed powder remotely on the injuries advances the recuperating system.
4. Antioxidants
Traditional medicine has used Clearing Nut Seeds a lot to treat arthritis, diabetes, problems with the GI tract, and other chronic conditions. Free radicals and oxidative stress are suspected in these non-communicable diseases.
Clearing Nut Seed is a good source of natural antioxidants for our body because it is rich in tannins that work to reduce oxidative stress and free radical damage to our cells.
5. Treating Jaundice
An effective treatment for anemia-related swelling, rhinitis, and jaundice is clearnut seed powder mixed with honey. Clearing nuts is likewise an intense diuretic. It advances pee in patients with low pee yield.
6. Improve digestion
Nuts have a lot of benefits for the digestive system. The powder of clearing nuts seeds is given in modest quantities to treat heartburn and the runs. It is additionally useful for individuals managing miniature nourishment.
Clearing nuts is a strong Ayurvedic spice that is utilized in the treatment of different sicknesses including jaundice, diabetes, and eye issues. Sadly, few people are aware of the amazing health benefits of clearing nuts. Thus, the time has come, we are familiar this Ayurvedic spice and uses it to serve our wellbeing.
7. Anti-inflammatory
In the customary arrangement of medication, Clearing Nut seeds were utilized for different diseases including irritation, and diabetes. Clearing Nut seeds contain anti-inflammatory substances such as steroids, triterpenoids, saponins, and polyphenols, according to research.
8. Regulate blood glucose level
In Ayurveda, Clearing Nut is a potent remedy for diabetes. In Madras, India the seeds are customarily utilized in treating diabetes. It has been demonstrated through research that one or more of the plant extract’s anti-diabetic compounds improve diabetic conditions, and that seed extract aids in the regulation of blood sugar levels.
9. Boost immunity
We need to keep our immune systems in check during this pandemic, and several nutritional supplements with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties have been shown to boost the immune system. Hence, in the right blend of these pharmacological exercises fixings as a food supplement might assist with helping the resistant framework, forestall infection spread, and restorative help against Coronavirus.
Traditional uses and benefits of Clearing Nut
- Seeds that are easy to digest have been shown to clear water, alleviate heat and thirst, neutralize poison, treat eye infections, and eradicate germs.
- To treat eye disorders, improve vision, and eliminate blood spotting from the whites of the eyes, paste made from ground seeds is applied topically in a circle around the eyes.
- When joined with honey it is applied topically in a circle around the eyes for waterfalls.
- Combination of seed glue with fluid yogurt taken for seven days is viewed as a remedy for ongoing, treatment-safe loose bowels.
- Combination of milk and seed glue is given as a solution for gonorrhea.
- Combination of seed debris and sugar is taken to reduce draining hemorrhoids.
- Glue made with refined water is utilized to treat unreasonable pee.
- Dysentery is treated and vomiting is induced with powdered seed coats.
- In India, pain caused primarily by internal injury is treated locally with root paste.
- Seed is utilized for a tonic, demulcent, stomachic, and narcotic, emetic and furthermore for loose bowels, diarrhea, gonorrhea, and eye inconveniences.
- Eye pain and epilepsy can be treated with leaves.
- Seeds can be used to treat a variety of ailments, including diabetes, bronchitis, chronic diarrhea, gonorrhea, leucorrhea, stomach issues, liver and kidney issues, and more.
- The vapor of a root decoction is inhaled to treat venereal diseases, and pounded leaves are used to treat watery and aching eyes in Tanzania.
- Cough is treated with roots and leaves decoction.
Seeds are utilized for the treatment of a scope of grievances including strangury, kidney and bladder stones, and diabetes and eye sicknesses. - Cantleyine, a monoterpene alkaloid isolated from the root bark, has been shown to relax isolated smooth muscles in the trachea and may be the active ingredient responsible for the anti-asthmatic and coughing properties.
- A fluid concentrate of the seeds has shown huge hepato-defensive movement.
- The seeds’ methanol extract had a diuretic and anti-diarrheal effect on castor oil-induced diarrhea.
- To treat allergies, a paste made from bark and other herbs and lime juice is applied to the skin.
- Fruits are helpful for eye diseases, thirst, poisoning, and hallucinations, while roots treat leucoderma.
- In Malawi a leaf decoction is taken to treat epilepsy.
- In Zambia the fume of a root decoction is breathed in to treat colds.
- In Zimbabwe a decoction of roots and leaves is taken to treat hack.
- Pounded fruits are used as fish poison in Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and South Africa, and crushed bark is also used in Zimbabwe.
- In Tanzania and Zambia the wood is utilized to make apparatus handles. The seeds are used to clean muddy water in Asia.
Additionally, it is used for sore throats. - In customary clinical frameworks, seeds utilized for treatment of hepato-pathy, gastro-pathy, nephropathy, gonorrhea, leucorrhea, loose bowels, renal and vesicle stones, diabetes.
- Lime juice and powdered stem bark are used to treat cholera.
- In cases of urinary disorders and urine retention, seed paste and tender coconut milk may be consumed internally.
Seeds powder blended in with honey is applied to bubbles to hurry decay. - Powder with milk is utilized in sensitive eyes.
Medicinal uses
- To treat a variety of eye conditions, the seeds are rubbed into a clean stone, and the paste is used as collyrium.
- For improved wound healing, the seed powder is applied over the wound in conjunction with the appropriate amount of honey.
- Glue of the root is applied over the skin region impacted with dermatitis.
- Powder of clearing nut seeds is given in a portion of 3-4 gm. to treat diarrhea and indigestion.
- In order to treat renal calculi and urinary incontinence, 40-50 milliliters of decoction of the seeds is administered.
- Decoction of the seeds with haridra assists with lessening and control glucose level.
- Poisoning can be treated with the seed decoction.
- Powder of the seeds with honey or the decoction of the seed is consumed in a portion of 40 ml to treat jaundice, rhinitis and expanding because of pallor.
- The force of the seed is blended in with a suitable amount of honey and applied overwound for better recuperating of it.
- Clearing Nut paste’s seeds are used as collyrium to treat a variety of eye conditions.
- Glue of the foundation of clearing Nut is applied over the skin region impacted by dermatitis.
Other Uses
- The wood is ideal for carts, shafts, agricultural implements, tool handles, etc., but not for carving.
- Polyelectrolytes in seed can be used as coagulants to clear up murky waters.
- In research center tests, direct filtration of turbid surface water with the seeds as a coagulant, created a significant improvement in its tasteful and microbiological quality.
- The yellowish-dim wood has obvious white markings.
- It is close-grained, extremely hard, and resistant to termites. However, it easily splits, making it unsuitable for carving.
- It is utilized to make trucks, shafts, horticultural executes, instrument handles and so forth.
- Ready seeds utilized for clearing sloppy water.
- Lord Thyagesar is associated with the tree.
Precautions
- Fish are poisoned with pounded fruits.
- Squashed bark is utilized as a fish poison.
- The plant can cause visual deficiency; alert is expected to keep away from contact with the eyes while utilizing it to treat eye problems and different circumstances.
- Avoid use during winter season.
Igini Tea – Strychnos potatorum
Igini Tea, which is made from the seeds of the Strychnos potatorum plant, is here to greet you. Our tea is a characteristic refreshment that has been utilized for quite a long time for its different
medical advantages. Igini Tea is an excellent addition to your daily routine for the following reasons:
1. Purifies kidneys: Igini Tea has traditionally been used to aid in the elimination of toxins from the body and support kidney function. The normal properties of Strychnos
potatorum seeds might assist with supporting solid urinary capability and advance kidney
wellbeing.
2. Controls glucose levels: Igini Tea might assist with directing glucose levels by
dialing back the retention of glucose in the circulation system. This makes it an extraordinary
refreshment for those hoping to keep up with sound glucose levels
3. improves digestion: Igini Tea is known to assist with mitigating the stomach related framework and
advance solid processing. Strychnos potatorum seeds’ natural compounds may alleviate indigestion, bloating, and other digestive issues.
4. Increments craving: Igini Tea might be a good solution for people who have trouble eating. The natural compounds found in the seeds of Strychnos potatorum may assist in increasing feelings of hunger and appetite.
To partake in the advantages of Igini Tea, basically blend a cup or two every day. Steep the tea in boiling water for 5 to 10 minutes. Add your favored sugar whenever wanted. As part of a healthy lifestyle, enjoy Igini Tea’s delicious and natural flavor.
Store in a cool, dry spot.
We appreciate you choosing Igini Tea.
| Weight | 0.3 kg |
|---|
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.
Be the first to review “New Igini Tea (Strychnos potatorum Tea/Clearing Nut Tea)”
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products
Sale
Organic Centrifuge Extra Virgin Coconut Oil – Oil ...
Rated 0 out of 5
0 out of 5
Sale
Dried Organic Sweet Jackfruit (Artocarpus heteroph...
Rated 0 out of 5
$17.50 – $62.32
Add to Compare
0 out of 5
Sale
Dried kakrol (Spiny Gourd/Momordica dioica)
Rated 0 out of 5
$23.06 – $85.75
Add to Compare
0 out of 5
Sale
100% Natural Wholesome Granola with VCO 300g Glass
Rated 0 out of 5
0 out of 5


DHL Shipping Worldwide

Guaranteed Money Back in 7 days return.

3 Day Returns in case u change your mind.
Dry Fish – Bala Karawala
$4.30


Espresso bean/Coffee Beans (Gr...
$33.62 – $45.90



























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.