Costaceae.
A family of Monocots known as the Costus or Spiral ginger family.
Plants of the World Online recognises 7 genera with around 120 species.
The Costus genus has 70 species, Tapeinochilos 16, Hellenia 10, Chamaecostus 8, Dimerocostus 3, Paracostus 2
and Monocostus 1. Australia has 2 or 3 species.
The small to large perennial herbs have stems growing from underground stems or rhizomes.
Above ground stems can be prostrate or erect with some over 4 m long.
The round mostly unbranched stems are sometimes twisted spirally.
The lower part of each stem has just leaf sheaths while the upper part has the leaves.
The simple alternate leaves, on short petioles are spirally arranged in 1 rank.
The leaf bases form tubular sheaths around and down the stem with the edges closed.
There is a ligule (a narrow membranous flap) at the base of the petiole.
The blade is elliptic with a pointed tip, the veins are pinnate and the midrib is prominent.
Sometimes there is rosette of leaves under the inflorescence.
The single Monocostus species has solitary flowers in the leaf axils.
All the other genera have an inflorescence that is terminal or on short leafless side shoots.
These inforescences are a spike that can be condensed into a short dense head or be more elongated and cone-like.
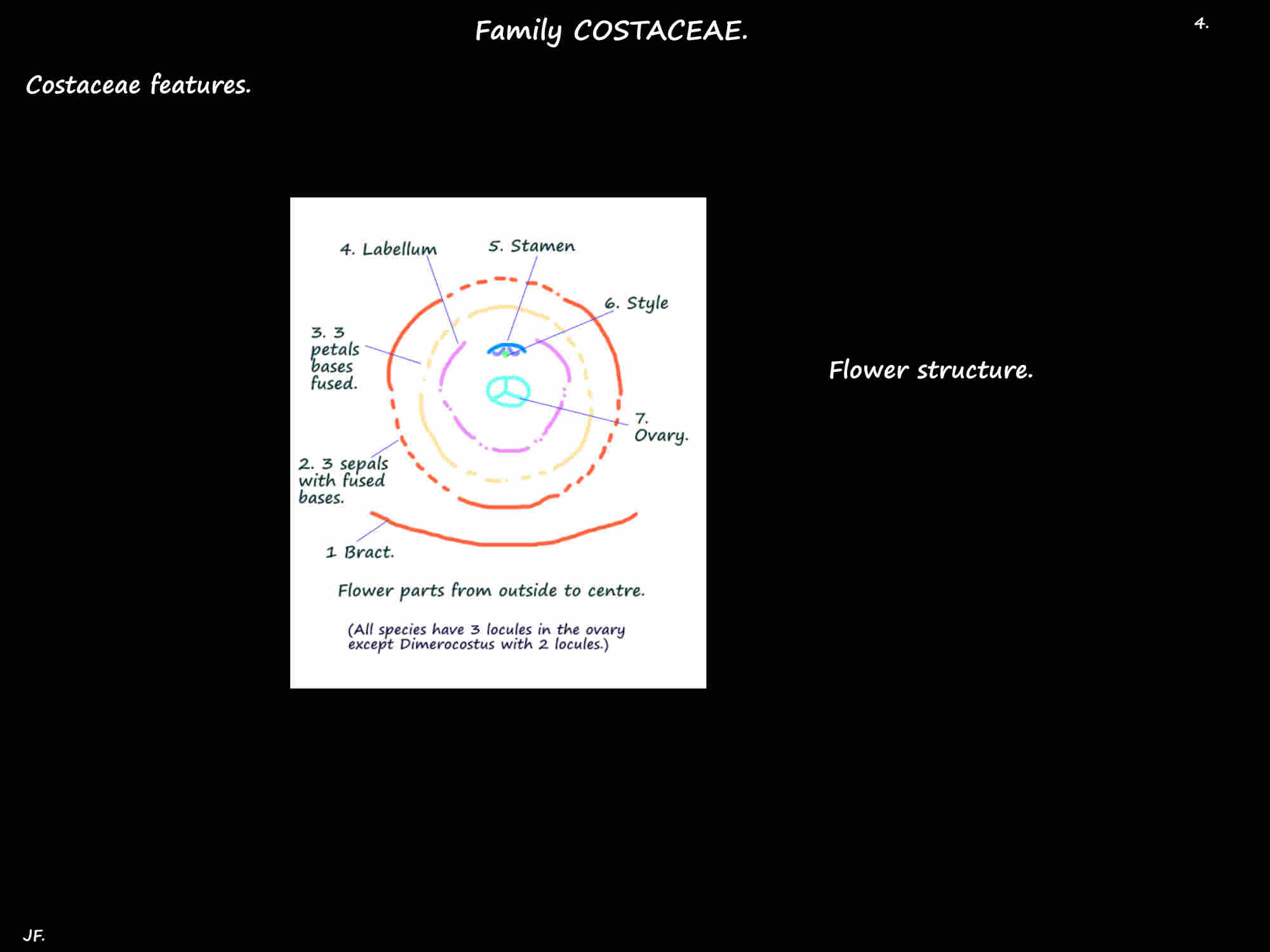
Overlapping spirally arranged bracts each hold 1 or 2 flowers.
The bracts can be soft or woody and they may have a spine at the tip.
Mostly red or red-brown they can also be orange, green or yellow.
There may be small bracteoles at the base of each flower.
The sepals form a tube with 2 or 3 short pointed lobes that may be similar or different.
It is often split down one side.
The 3 petals, often longer than the sepals are fused into a tube with 3 unequal lobes.
The bell or funnel-shaped corolla can be red yellow or cream.
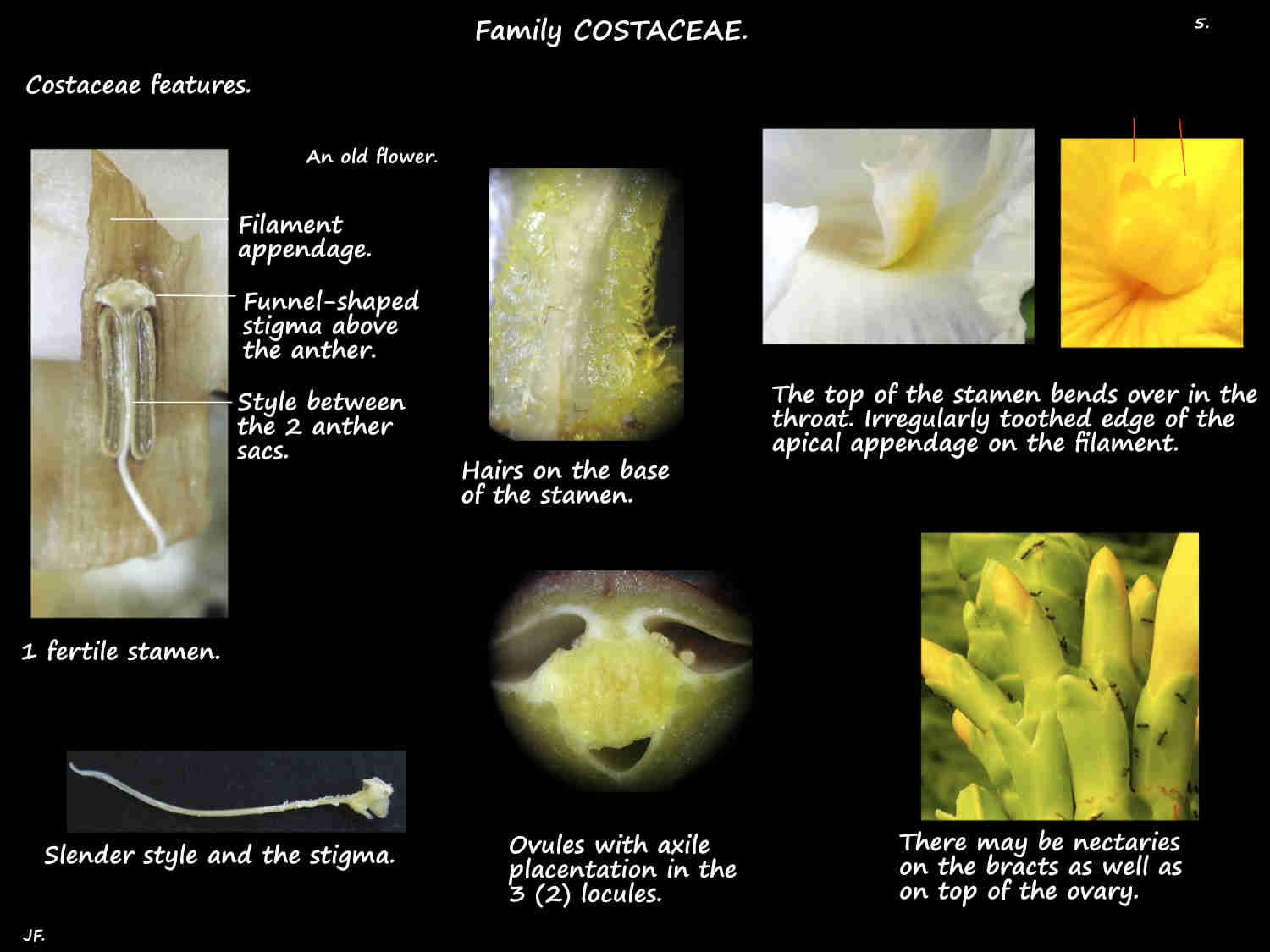
There is one fertile stamen that may be petal-like with a wide filament that bends across the top of the tube.
The anther has 2 thecae or pollen sacs that open inwards through longitudinal slits.
The three staminodes in the outer whorl and the 2 in the inner are fused to form a lobed petal-like labellum.
It may be spreading or tubular and the edge may be wavy and crinkled.
The size varies from small and inconspicuous to longer than the corolla.
It can be white, yellow, red, orange, pink or purple sometimes with coloured markings on the sides.
The filament base is fused to the base of the labellum.
The inferior ovary has 3 locules each with ovules in 2 rows having axile placentation.
The style lies between the anther sacs and it has a variously shaped stigma.
There are 3 septal nectaries on top of the ovary.
The fruit is often a capsule that breaks into the locules or anywhere.
Fruit are occasionally a berry.
The dark brown or black seeds have a white or yellow aril (a fleshy appendage beside the point of attachment of the seed).
They differ from the closely related Zingiberaceae or Ginger family by having leaves in 1 rank and closed leaf sheaths.
J.F.